Now that VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 is available, more and more people are trying to understand its new features and improvements. To help with that, I’ll create a series of two articles to explain the main changes that are coming.
In this first article, I’m going to talk about some of the new features in the ESXi 9.0 kernel.
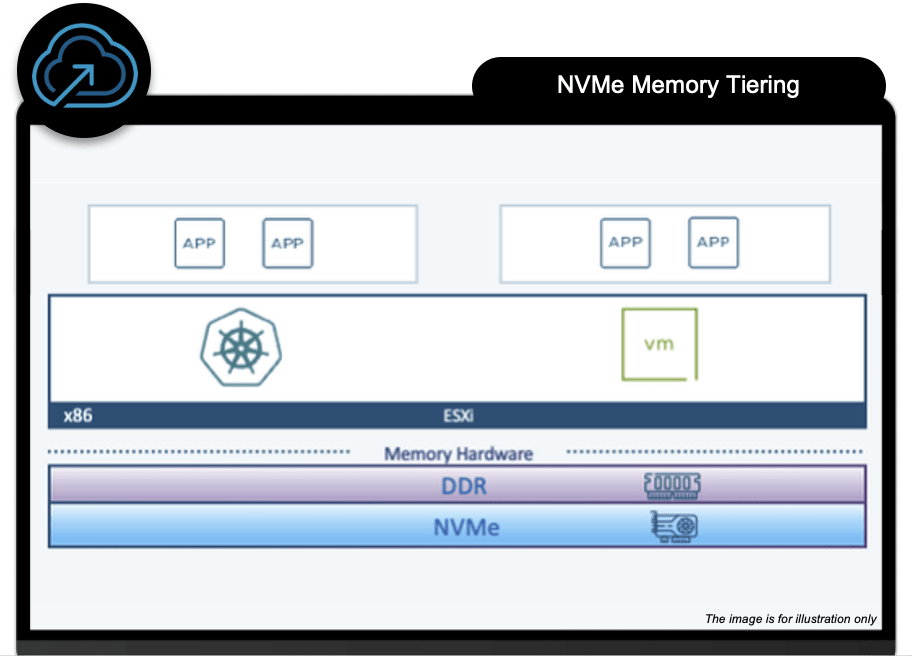
Advanced NVMe Memory Tiering
With this feature, it’s now possible to expand the memory capacity of an ESXi host using NVMe drives installed in the server itself.
This extension acts as a second layer of memory. ESXi uses the main memory (DRAM) for high-performance workloads, while the second memory layer (NVMe) handles the rest.
The result is: We can run more VMs or containers per host without needing to invest in additional hardware.
vSAN Global Deduplication
vSAN now supports global deduplication across the entire cluster.
What does this mean? In a nutshell, what deduplication does is find identical blocks of data and replaces them with metadata that points to those blocks, freeing up storage space.
With global deduplication, the whole cluster is considered for optimization, increasing space savings opportunities.
Another improvement is how the process is performed. Instead of running during data write operations (which can impact performance), deduplication now runs as a post-processing task in the background, using CPU idle time — so application performance isn’t affected.

Enhanced Data Paths
There’s a new packet forwarding stack designed to deliver much higher performance — up to 3× better throughput, packet rate, latency, and CPU utilization. Click here for more details..
This enhancement is especially relevant for modern workloads like AI pipelines, microservices, and highly distributed applications, which depend on efficient networking.
Conclusion
These are just a few of the improvements introduced in the ESXi kernel with VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0. There are many benefits, and more will become clear as we explore the ecosystem further.
Hope you like it!


Leave a comment